
Hillary Stires, PhD
I received my PhD from Rutgers University in Endocrinology and Animal Biosciences in 2016 under the mentorship of Dr. Wendie Cohick then did three years of a postdoc in the T32 Tumor Biology Program at Georgetown University's Lombardi Comprehensive Cancer Center under the mentorship of Dr. Rebecca Riggins.
While doing my PhD I helped re-organize the General Biology Lab Course to ultimately teach over 800 students per semester. At Georgetown, I helped to re-establish the Georgetown University Postdoctoral Association.
My overall research goal was to understand the role of hormone signaling in endocrine resistance and metastasis in estrogen receptor-positive (ER+) breast cancer.
Postdoc Work
The Role of ER in HER2+/ ER+ (Triple Positive) Breast Cancer
There are over 2 million new case of breast cancer diagnosed per year worldwide and breast cancer is the top cancer for females in the majority of countries in the world according to the World Health Organization. There are approximately 522,000 deaths caused by breast cancer every year worldwide.

Breast cancer is subdivided into three major classes based off of receptor status: 1) ER+ 2) HER2+ and 3) triple-negative.
There are successful treatment options for ER+ breast cancer including (not a complete list):
-
aromatase inhibitors
-
Arimidex (anastrozole)
-
Aromasin (exemestane)
-
Femara (letrozole))
-
-
selective ER modulators (SERM)
-
Tamoxifen
-
-
selective ER degraders (SERD)
-
Faslodex (fulvestrant; ICI 182-780)
-
and for HER2+ breast cancer including:
-
antibodies
-
Herceptin (trastuzumab)
-
Perjeta (pertuzumab)
-
-
small molecule inhibitors
-
Tykerb (lapatinib)
-
-
antibody drug conjugates
-
Kadcyla (TDM1)
-
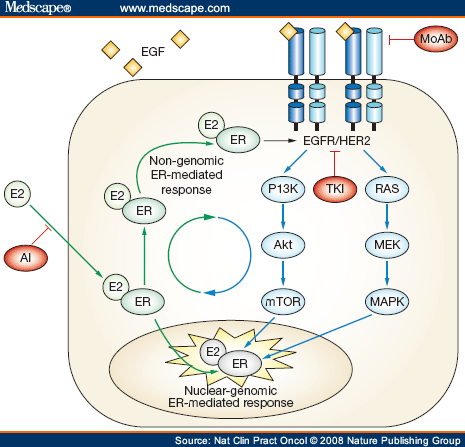
However, when a patient has triple-positive disease, it is not clear which treatments clinicians should use first or in combination. While American Society of Clinical Oncology (ASCO) guidelines suggest using HER2-targeted therapy for triple-positive breast cancer, patients with tumors that are ER+ and HER2+ given HER2-targeted therapy have a lower pathologic complete response (pCR) compared with those who are HER2+ but ER-negative. These results suggest the presence of ER influences efficacy of HER2-targeted therapy.
It is well known that the HER2 and ER pathways overlap and the figure on the left from Aleix Prat and José Baselga demonstrates some of the ways this occurs. Using cell models, scientists have demonstrated that if one of the pathways is blocked, the other pathway compensates. For example, long-term treatment with the small molecule inhibitor lapatinib in the UACC812 cell line that is HER2+ and ER-negative leads to increased ER expression and cells that were originally resistant to the SERD fulvestrant become responsive. Similarly, when the ER+ and HER-nonamplified cell line MCF7 is manipulated to overexpresses aromatase is then treated with an aromatase inhibitor long-term, the HER2 pathway is activated and xenograft tumors become responsive to trastuzumab. These results suggest these pathways can compensate for one another when one is blocked. What happens when both receptors are present is less clear.
I was selected to be a Gibco Cell Culture Hero and presented a webinar about this work that can be viewed here. I also recorded a podcast with Cell Culture Dish that can be listened to here.
Endocrine Resistance in Invasive Lobular Carcinoma
The two most common ways to define breast cancer are by receptor status and by molecular subtype, however, a third less understood difference in breast tumors is histopathology, which considers microscopic structure of the tumor and is subdivided into invasive ductal carcinoma (IDC) and invasive lobular carcinoma (ILC; see figures→). ILC accounts for 15% of breast cancer cases, similar to the incidence of triple negative breast cancer. IDC and ILC differ in a few key ways: ILC is less responsive to chemotherapy and tends to be multi-focal with metastasis to unusual sites. Approximately 90% of ILC is ER-positive and is thus treated with anti-estrogens, however recent data suggests women with ILC develop Tamoxifen resistance at a higher rate than IDC. It is not known why patients with ILC have greater likelihood of Tamoxifen resistance than IDC. Dr. Riggins established an ILC model of Tamoxifen resistance from the parental Sum44 cell line termed LCCTam, which we use to understand Tamoxifen resistance specifically in ILC. We have recently published a comprehensive analysis of these cell lines. Our results suggest that the MAPK pathway and metabotropic glutamate receptor (GRM/mGluR) pathway are altered in the resistant line. Ongoing studies are using pharmacologic inhibition of these pathways to demonstrate restoration of anti-endocrine inhibition.


ILC
IDC
Georgetown University Postdoctoral Association (GU PDA)
We re-established the GU PDA in January 2017 with the mission to enhance the quality of the postdoctoral experience by providing a community for postdoctoral fellows. After serving as a co-chair for the first year and a half, I have passed the reigns and continue to participate in GU PDA activities. The GU PDA aims to prepare postdoctoral fellows for the next steps of their careers through networking, professional branding, and mastering skills necessary to search for and obtain a job. Following our symposium last year, I wrote this piece on our establishment. Dr. Caleb McKinney followed it up with an article in the POSTDOCKet, the National Postdoc Association's monthly newsletter.
For more information about GU PDA, please visit their website!
PhD Thesis Work
Peroral Estradiol is Sufficient to Induce Carcinogen-Induced Mammary Tumorigenesis in Ovariectomized Rats without Progesterone
The interactions of estradiol (E2) and progesterone (P4) in breast cancer are complex. The rat chemical carcinogen model has been widely used to study the effects of E2 but conclusions on the additive effect of E2 and P4 are less clear. A newer method of hormone administration mixes hormones with nut butter for peroral consumption allowing for a less stressful method of administration with lower spikes in serum E2 levels. The goal was to determine whether E2 alone can drive carcinogen-induced tumors in ovariectomized (OVX) rats or if P4 is also required using this method of hormone administration. After 26 weeks, tumor incidence was similar in sham, E2, and E2 + P4 animals indicating that E2 was sufficient to induce tumorigenesis when hormone levels were normalized by this method. Immunohistochemistry indicated that tumors from these animals had similar proliferative rates and ER status, though PR status tended to be higher in the E2 + P4 group. Results from this study were published in PLoS One.
Mechanisms That Drive Increased Mammary Tumorigenesis in Rats Exposed To Alcohol in Utero
The Developmental Origins of Health and Disease hypothesis suggests that exposure to various environmental factors during critical periods of development can influence disease states later in life, including breast cancer. Alcohol exposure in utero can enhance tumor development in offspring in rats, and tumors that do arise display a more aggressive phenotype. In an effort to find treatment options and increase warnings as part of a prevention strategy, it is important to elucidate mechanisms of how alcohol exposure during pregnancy can influence cancer development in the young. For more information, please view our book chapter and publication.
Course Description: In Biological Research Laboratory, students conduct research in two conceptual area, aquatic ecology and DNA sequencing. Students design and conduct a novel research project in aquatic ecology. Students also isolate and sequence DNA from an organism they collect on a field trip to a local water body. The two research projects are linked ultimately via phylogenetics. Through these projects, students are exposed to the process of science and tools and techniques used in science.
When I was a graduate student at Rutgers, I was also a teaching assistant for general biology. During the Spring semester of my second year, I was asked to work with a group of 2 other teaching assistants, the course directors, and lab staff to re-write the laboratory portion of the biology course. We mapped the flow of the course, wrote the lab manual, prepared powerpoint presentations, and designed exams. I also helped re-design the physical lab space with a contractor to best help the needs of the program. Over the next two years, we piloted the program with 6 classes per semester. During the Spring of my 4th year of graduate school, I served as head teaching assistant when we launched the course to serve over 800 students by 18 teaching assistants. Along with the teaching assistants who redesigned the course with me, I received the Rutgers University School of Arts and Science Award for Distinguished Contributions to Undergraduate Education for our efforts.